Prostate Cancer Awareness Month, observed every September, serves as a crucial reminder about the importance of prostate health. It’s a time to spread awareness, offer support to those affected, and emphasize the need for early detection. Prostate cancer remains one of the most common cancers among men, and raising awareness can make a significant difference in outcomes.
Understanding Prostate Cancer
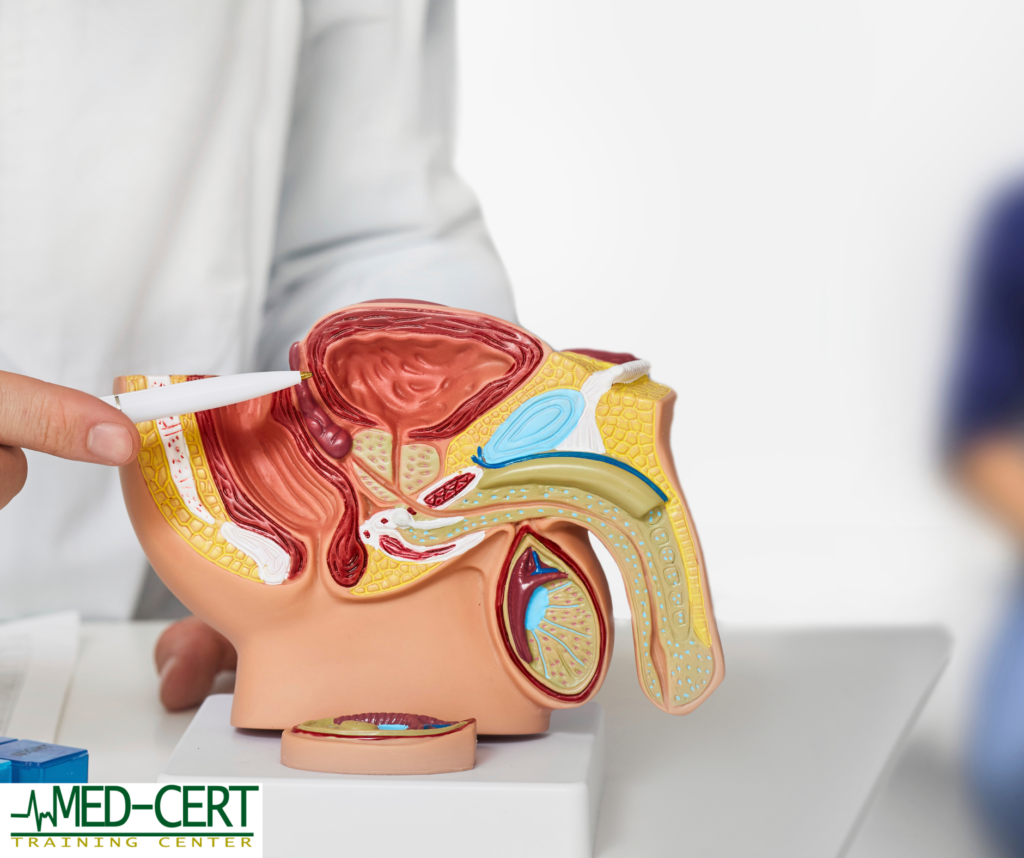
Prostate cancer begins in the prostate gland, a small organ located below the bladder and in front of the rectum. This gland plays an essential role in male reproductive health, contributing to the production of semen. Like other cancers, prostate cancer occurs when cells in the prostate grow uncontrollably.
The American Cancer Society estimates that one in eight men will be diagnosed with prostate cancer during their lifetime, with about 288,300 new cases expected in the U.S. in 2024 alone. While these numbers may seem staggering, the silver lining is that prostate cancer is highly treatable, especially when detected early.
Who Is at Risk?
Certain risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing prostate cancer. Some of the most common risk factors include:
Age: The risk of prostate cancer increases with age. It’s more common in men over 50, and most cases are diagnosed in men aged 65 and older.

Family History: Men with a close family member (father or brother) who has had prostate cancer are at higher risk.

Race: African-American men face a higher risk of developing prostate cancer and are more likely to be diagnosed at an advanced stage.

Diet and Lifestyle: A diet high in red meat and processed foods, coupled with a lack of exercise, may increase the risk of developing prostate cancer.
Understanding these risk factors is critical to promoting early detection and encouraging at-risk populations to seek regular screenings.
The Importance of Early Detection
Early detection is key to effectively treating prostate cancer. In many cases, prostate cancer grows slowly, which allows for more treatment options and a better prognosis. Regular screening can help identify cancer in its early stages when it’s most treatable.
The two main screening tests for prostate cancer are:
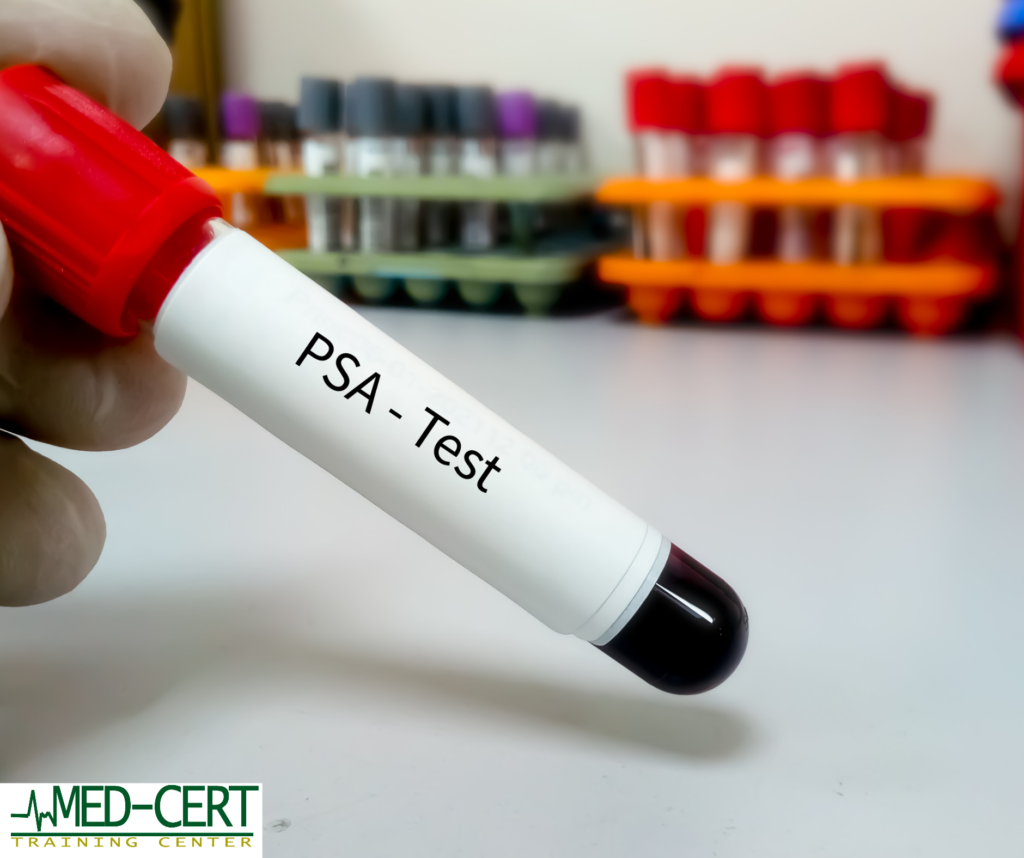
Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Test: This blood test measures the level of PSA, a protein produced by the prostate. Elevated PSA levels may indicate the presence of cancer, although high levels can also result from other non-cancerous conditions.

Digital Rectal Exam (DRE): During a DRE, a healthcare provider manually examines the prostate through the rectum to check for abnormalities in size, shape, or texture.
While these tests can be lifesaving, they are not without controversy. False positives, false negatives, and over diagnosis are concerns that should be weighed when considering routine screening. It’s essential to consult with your healthcare provider to determine when and how often you should be tested.
Treatment Options for Prostate Cancer
Treatment for prostate cancer depends on several factors, including the cancer’s stage, the patient’s age, and overall health. The main treatment options include:

Active Surveillance: For men with early-stage prostate cancer that is slow-growing, doctors may recommend regular monitoring instead of immediate treatment. This approach helps avoid unnecessary treatment and potential side effects.

Surgery: The most common surgical procedure is a radical prostatectomy, where the entire prostate gland is removed. This option is typically recommended for cancer that hasn’t spread beyond the prostate.
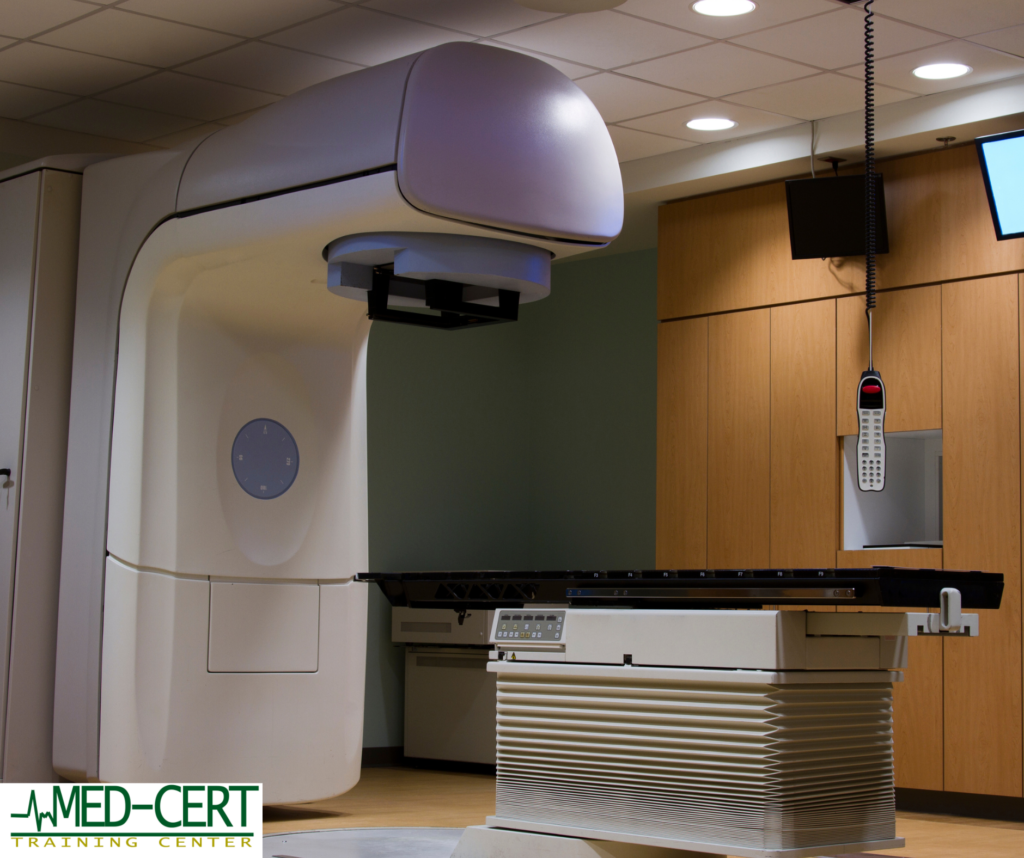
Radiation Therapy: This treatment uses high-energy rays to target and kill cancer cells. Radiation may be used in conjunction with surgery or as the primary treatment.

Hormone Therapy: Prostate cancer cells rely on male hormones (androgens) to grow. Hormone therapy reduces the levels of these hormones, slowing the growth of cancer.
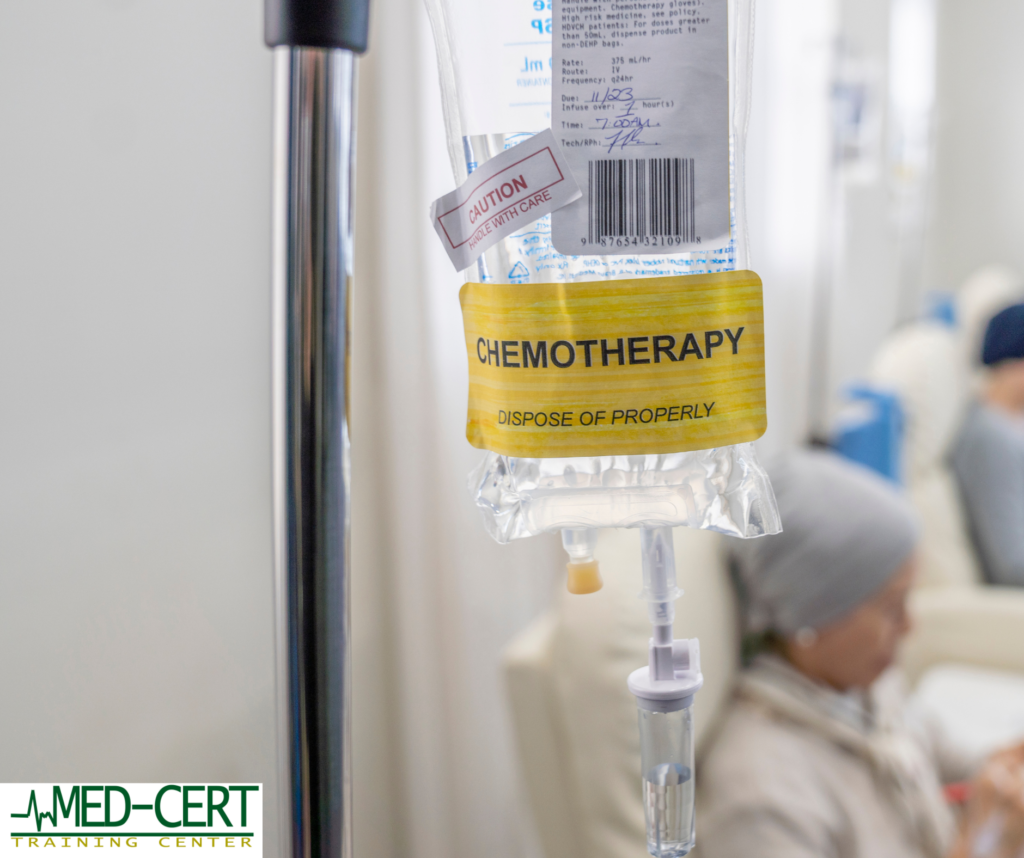
Chemotherapy: While less common for early-stage prostate cancer, chemotherapy may be used for advanced or recurrent cancer.
Side effects of treatment vary and may include urinary incontinence, erectile dysfunction, fatigue, and bowel issues. It’s important to discuss potential side effects with your doctor to make an informed decision about your treatment plan.
Supporting Prostate Cancer Research and Advocacy
Prostate Cancer Awareness Month is also an opportunity to support ongoing research, education, and advocacy efforts. Many organizations, such as the Prostate Cancer Foundation (PCF) and ZERO – The End of Prostate Cancer, are dedicated to finding new treatments, supporting patients, and advocating for policies that improve access to care.
Getting involved in these efforts can make a difference. Consider participating in fundraising events, donating to research organizations, or simply sharing information about prostate cancer with your family and friends. By raising awareness, you can help others understand the importance of early detection and prostate health.
Prostate cancer is a serious disease, but it is highly treatable when detected early. Prostate Cancer Awareness Month offers an opportunity to learn more about this condition, encourage regular screenings, and support those affected by the disease. If you’re a man over the age of 50 or have risk factors, now is the perfect time to schedule a conversation with your healthcare provider about prostate cancer screening.
Together, through awareness and early detection, we can continue to reduce the impact of prostate cancer and save lives. Remember, staying informed is the first step toward protecting your health.
